Hobart's funnies, the
special weapons
In 1944 the beaches from Norway
all the way down to the Spanish border where lined with obstacles of all
sorts from the huge steel Belgian gates up to the poles with mines on
top of them.
The Allies made numerous air
reconnaisance pictures of these obstacles and the reconstructed them in
England. 79th Armoured division had orders to come up with a number of
special weapons to help the landing forces to overcome the obstacles on
the beaches.
This lead to the following weapons.
Sherman A4-D4 DD (Duplex
Drive)
 This
was an amphibious tank, driven by two propellors on the back of the tank.
The tank had a boat shaped platform. On this platform a canvas construction
was made. The canvas could be lifted from in side the tank by two gas
cellinders. The canvas when fully elevated came one metre higher than
the waterline. This ment that the tank could only float in quiet water.
The tank could reach 7 kilometres an hour while in the water. In the water
the tank looked like a very small fragile boat so it probably wouldn't
attract much attention from the German defenders before it drove onto
the beach. The tank was an invention or the engineer Nicolas Strauller. This
was an amphibious tank, driven by two propellors on the back of the tank.
The tank had a boat shaped platform. On this platform a canvas construction
was made. The canvas could be lifted from in side the tank by two gas
cellinders. The canvas when fully elevated came one metre higher than
the waterline. This ment that the tank could only float in quiet water.
The tank could reach 7 kilometres an hour while in the water. In the water
the tank looked like a very small fragile boat so it probably wouldn't
attract much attention from the German defenders before it drove onto
the beach. The tank was an invention or the engineer Nicolas Strauller.
 |
The
canvas construction has been lifted on this DD Tank that stands
in the Bovington Tank museum in Southern England. The window in
the canvas is only for display functions, made by the museum. the
driver of the tank had to stand on top of the turret to see where
he was going when the tank was in the water.
Some
troops thought that the DD stood for Donald Duck.
|
Sherman M4-D4 Crab flegeltank.
 This
tank saw it's first action in North Africa, however D-day would be the
first operation in which it would be used on a large scale. The idea for
this tank cam form the South African major A.S. du Toit. The crab was
a normal Sherman tank with the one exception that it had a large drum
in front of it with chaines attached to the drum. The tank driver could
spin the drum, so that the chains would bang on the ground in front of
the tank. These chaines would explode any mines that might be their on
a safe distance in front of the tank. The tank could clear a safe passage
through a minefield of three metres wide. On the back-end of the tank
two containers with chalk where attached. With the chalk the tank could
mark the path it had cleared. This
tank saw it's first action in North Africa, however D-day would be the
first operation in which it would be used on a large scale. The idea for
this tank cam form the South African major A.S. du Toit. The crab was
a normal Sherman tank with the one exception that it had a large drum
in front of it with chaines attached to the drum. The tank driver could
spin the drum, so that the chains would bang on the ground in front of
the tank. These chaines would explode any mines that might be their on
a safe distance in front of the tank. The tank could clear a safe passage
through a minefield of three metres wide. On the back-end of the tank
two containers with chalk where attached. With the chalk the tank could
mark the path it had cleared.
Churchill
MK-III Bobbin
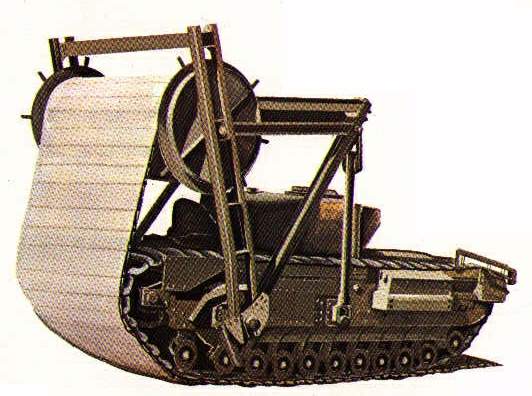 Special
units of the Britsh navy landed on the Normandy beached and took samples
of the sand with them. From this the Intelligence concluded that at least
part of the beach would be to soft to carry the heavy weight of tanks.
The Bobbin was a Churchill tank that would lay a large wooden carpet on
the beach. The carpet was 3 metres wide and 110 metres long. The carpet
would also cover the barbed wire which would facilitate the infantry in
crossing the barbed wire. After the whole carpet was laid, the tank could
get rid of the drum that had carried the carpet, by blowing up small explosives.
The churchill tank could then be of further service as a regular tank. Special
units of the Britsh navy landed on the Normandy beached and took samples
of the sand with them. From this the Intelligence concluded that at least
part of the beach would be to soft to carry the heavy weight of tanks.
The Bobbin was a Churchill tank that would lay a large wooden carpet on
the beach. The carpet was 3 metres wide and 110 metres long. The carpet
would also cover the barbed wire which would facilitate the infantry in
crossing the barbed wire. After the whole carpet was laid, the tank could
get rid of the drum that had carried the carpet, by blowing up small explosives.
The churchill tank could then be of further service as a regular tank.
Churchill
MK-VII Crocodile
 On
this tank the machinegun was replaces by a flamethrower. This canon was
fuelled by a cart which the tank towed behind it. This cart contained
1800 litres of pressured (stikstof?). The crocodile could produce a beam
of frames upto 120 metres. This weapon would prove to be very effective
against small bunkers and machinegun posts. On
this tank the machinegun was replaces by a flamethrower. This canon was
fuelled by a cart which the tank towed behind it. This cart contained
1800 litres of pressured (stikstof?). The crocodile could produce a beam
of frames upto 120 metres. This weapon would prove to be very effective
against small bunkers and machinegun posts.
Churchill
MK-III AVRE (Armoured Vehicle Royal Engineers)
 The
tank is equiped with a 25-pound Pertard-mortar. It had a range of two
hundred metres. This tank could carry an SBG, a "Small Box Glider",
this was a small bridge element in order to bypass tankwalls, and didges.
In stead of a SBG, huge bundles of wood where also carried by these tanks
for the same purpose. The
tank is equiped with a 25-pound Pertard-mortar. It had a range of two
hundred metres. This tank could carry an SBG, a "Small Box Glider",
this was a small bridge element in order to bypass tankwalls, and didges.
In stead of a SBG, huge bundles of wood where also carried by these tanks
for the same purpose.
The British
and Canadians used all the types mentioned above on D-day. The Americans
only used the DD tank and as we shall see without succes.
<< BACK
|

 This
was an amphibious tank, driven by two propellors on the back of the tank.
The tank had a boat shaped platform. On this platform a canvas construction
was made. The canvas could be lifted from in side the tank by two gas
cellinders. The canvas when fully elevated came one metre higher than
the waterline. This ment that the tank could only float in quiet water.
The tank could reach 7 kilometres an hour while in the water. In the water
the tank looked like a very small fragile boat so it probably wouldn't
attract much attention from the German defenders before it drove onto
the beach. The tank was an invention or the engineer Nicolas Strauller.
This
was an amphibious tank, driven by two propellors on the back of the tank.
The tank had a boat shaped platform. On this platform a canvas construction
was made. The canvas could be lifted from in side the tank by two gas
cellinders. The canvas when fully elevated came one metre higher than
the waterline. This ment that the tank could only float in quiet water.
The tank could reach 7 kilometres an hour while in the water. In the water
the tank looked like a very small fragile boat so it probably wouldn't
attract much attention from the German defenders before it drove onto
the beach. The tank was an invention or the engineer Nicolas Strauller.
 This
tank saw it's first action in North Africa, however D-day would be the
first operation in which it would be used on a large scale. The idea for
this tank cam form the South African major A.S. du Toit. The crab was
a normal Sherman tank with the one exception that it had a large drum
in front of it with chaines attached to the drum. The tank driver could
spin the drum, so that the chains would bang on the ground in front of
the tank. These chaines would explode any mines that might be their on
a safe distance in front of the tank. The tank could clear a safe passage
through a minefield of three metres wide. On the back-end of the tank
two containers with chalk where attached. With the chalk the tank could
mark the path it had cleared.
This
tank saw it's first action in North Africa, however D-day would be the
first operation in which it would be used on a large scale. The idea for
this tank cam form the South African major A.S. du Toit. The crab was
a normal Sherman tank with the one exception that it had a large drum
in front of it with chaines attached to the drum. The tank driver could
spin the drum, so that the chains would bang on the ground in front of
the tank. These chaines would explode any mines that might be their on
a safe distance in front of the tank. The tank could clear a safe passage
through a minefield of three metres wide. On the back-end of the tank
two containers with chalk where attached. With the chalk the tank could
mark the path it had cleared. Special
units of the Britsh navy landed on the Normandy beached and took samples
of the sand with them. From this the Intelligence concluded that at least
part of the beach would be to soft to carry the heavy weight of tanks.
The Bobbin was a Churchill tank that would lay a large wooden carpet on
the beach. The carpet was 3 metres wide and 110 metres long. The carpet
would also cover the barbed wire which would facilitate the infantry in
crossing the barbed wire. After the whole carpet was laid, the tank could
get rid of the drum that had carried the carpet, by blowing up small explosives.
The churchill tank could then be of further service as a regular tank.
Special
units of the Britsh navy landed on the Normandy beached and took samples
of the sand with them. From this the Intelligence concluded that at least
part of the beach would be to soft to carry the heavy weight of tanks.
The Bobbin was a Churchill tank that would lay a large wooden carpet on
the beach. The carpet was 3 metres wide and 110 metres long. The carpet
would also cover the barbed wire which would facilitate the infantry in
crossing the barbed wire. After the whole carpet was laid, the tank could
get rid of the drum that had carried the carpet, by blowing up small explosives.
The churchill tank could then be of further service as a regular tank. On
this tank the machinegun was replaces by a flamethrower. This canon was
fuelled by a cart which the tank towed behind it. This cart contained
1800 litres of pressured (stikstof?). The crocodile could produce a beam
of frames upto 120 metres. This weapon would prove to be very effective
against small bunkers and machinegun posts.
On
this tank the machinegun was replaces by a flamethrower. This canon was
fuelled by a cart which the tank towed behind it. This cart contained
1800 litres of pressured (stikstof?). The crocodile could produce a beam
of frames upto 120 metres. This weapon would prove to be very effective
against small bunkers and machinegun posts. The
tank is equiped with a 25-pound Pertard-mortar. It had a range of two
hundred metres. This tank could carry an SBG, a "Small Box Glider",
this was a small bridge element in order to bypass tankwalls, and didges.
In stead of a SBG, huge bundles of wood where also carried by these tanks
for the same purpose.
The
tank is equiped with a 25-pound Pertard-mortar. It had a range of two
hundred metres. This tank could carry an SBG, a "Small Box Glider",
this was a small bridge element in order to bypass tankwalls, and didges.
In stead of a SBG, huge bundles of wood where also carried by these tanks
for the same purpose.